According to the latest edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) Manual, the formal recommendation on abstinence time for semen analysis is two to seven days. However, this period is not endorsed by the European Society for Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) and the Nordic Association of Andrology (NAFA), which limit abstinence time to a narrower interval, ranging from three to four days. These differences in criteria have led to the publication of several articles on the impact of the abstinence period on seminal parameters and / or clinical outcomes, with controversial results.
For this reason, Dr Piort Sokol from Dexeus Mujer has led a study that reviews the available evidence on this topic from the last 20 years. To do this, an electronic search was carried out in PubMed / MEDLINE. Only articles published in English and after 2010 were included. For consistent data, studies using WHO guideline values prior to their 5th edition (prior to 2010) were excluded.
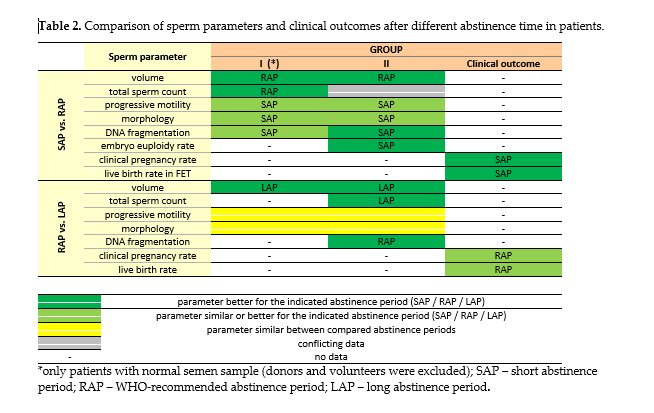
The results of the analysed studies indicate that the WHO abstinence recommendations may need revision, since a shorter ejaculatory abstinence interval appears to be associated with an improvement in sperm parameters, such as sperm DNA fragmentation, progressive motility, or morphology, while the evidence suggests a possible increased rates of embryonic euploidy. Based on the results obtained, the authors conclude that recommending patients a shorter abstinence period (less than 48 hours) before producing the sample could have positive effects both for some of the seminal parameters and for the treatment result.
Reference article:
The Effect of Ejaculatory Abstinence Interval on Sperm Parameters and Clinical Outcome of ART. A Systematic Review of the Literature
Sokol, P.; Drakopoulos, P.; Polyzos, N.P.
J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3213.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153213